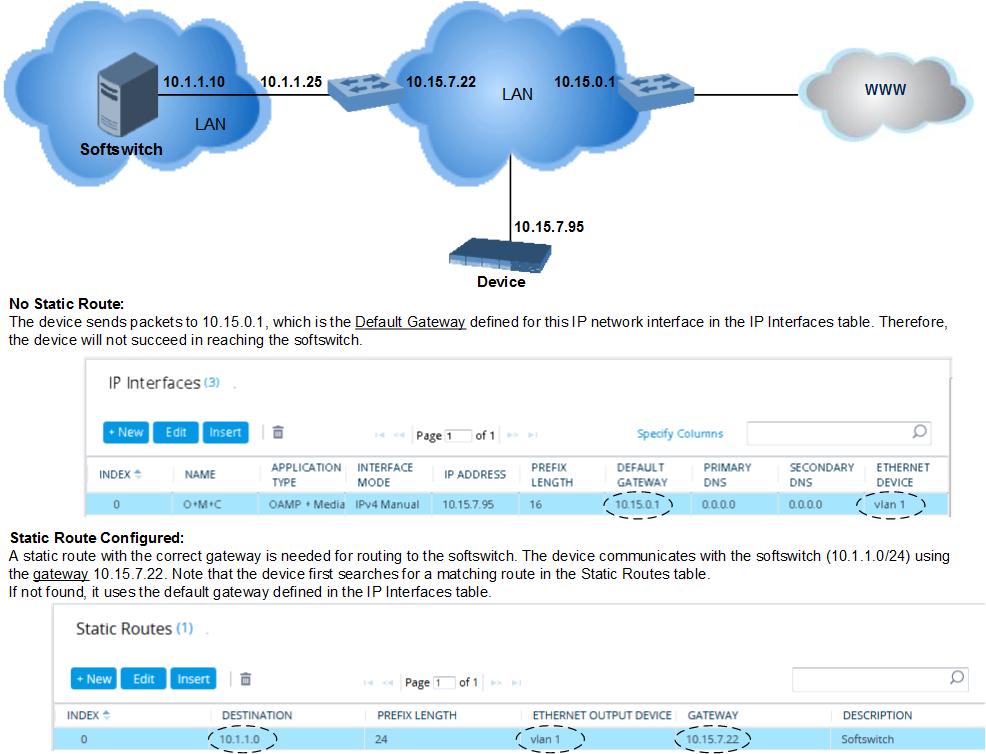
Configuration Example of Static IP Routes
An example of the use for static routes is shown in the figure below. In the example, the device needs to communicate with a softswitch at IP address 10.1.1.10. However, the IP network interface from which packets destined for 10.1.1.10 is sent, is configured to send the packets to a Default Gateway at 10.15.0.1. Therefore, the packets do not reach the softswitch. To resolve this problem, a static route is configured to specify the correct gateway (10.15.7.22) in order to reach the softswitch.
Note the following configuration:
| ■ | The static route is configured with a subnet mask of 24 (255.255.255.0), enabling the device to use the static route to send all packets destined for 10.1.1.x to this gateway and therefore, to the network in which the softswitch resides. |
| ■ | The static route in the Static Routes table must be associated with the IP network interface in the IP Interfaces table. This is done by configuring the |
| ■ | The static route's Gateway address in the Static Routes table is in the same subnet as the IP address of the IP network interface in the IP Interfaces table. |