Configuring the Device's LDAP Cache
The device can optionally store LDAP queries of LDAP Attributes for a searched key with an LDAP server and the responses (results) in its local cache. The cache is used for subsequent queries or in case of LDAP server failure. The benefits of this feature include the following:
| ■ | Improves routing decision performance by using local cache for subsequent LDAP queries |
| ■ | Reduces number of queries performed on an LDAP server and corresponding bandwidth consumption |
| ■ | Provides partial survivability in case of intermittent LDAP server failure (or network isolation) |
The handling of LDAP queries using the device's LDAP cache is shown in the flowchart below:
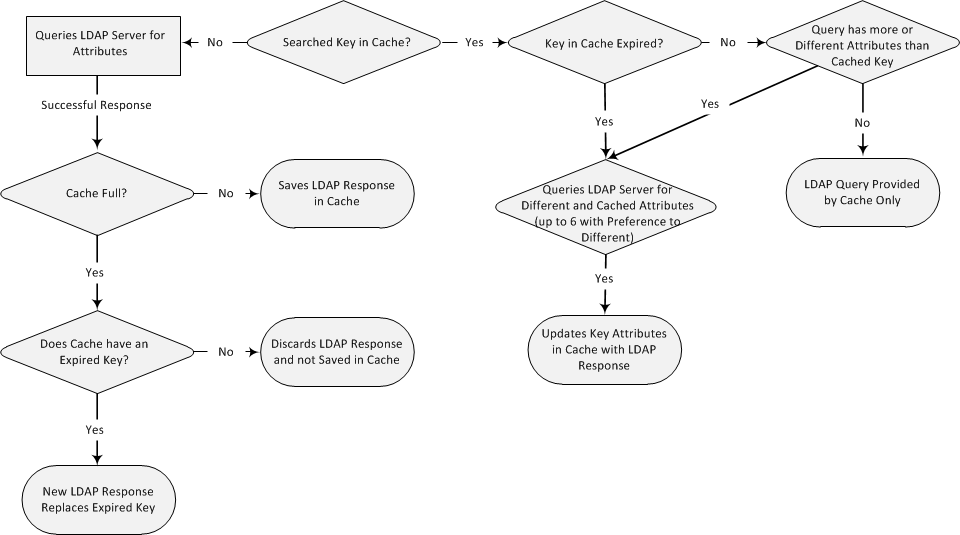
If an LDAP query is required for an Attribute of a key that is already cached with that same Attribute, instead of sending a query to the LDAP server, the device uses the cache. However, if an LDAP query is required for an Attribute that doesn't appear for the cached key, the device queries the LDAP server, and then saves the new Attribute (and response) in the cache for that key.
If the device queries the LDAP server for different Attributes for a cached key, the device also includes already cached Attributes of the key, while adhering to the maximum number of allowed saved Attributes (see note below), with preference to the different Attributes. In other words, if the cached key already contains the maximum Attributes and an LDAP query is required for a different Attribute, the device sends an LDAP query to the server for the different Attribute and for the five most recent Attributes already cached with the key. Upon the LDAP response, the new Attribute replaces the oldest cached Attribute while the values of the other Attributes are refreshed with the new response.
The following table shows an example of different scenarios of LDAP queries of a cached key whose cached Attributes include a, b , c, and d, where a is the oldest and d the most recent Attribute:
Example of LDAP Query for Cached Attributes
|
Attributes Requested in New LDAP Query for Cached Key |
Attributes Sent in LDAP Query to LDAP Server |
Attributes Saved in Cache after LDAP Response |
|---|---|---|
|
e |
e, a, b, c, d |
e, a, b, c, d |
|
e, f |
e, f, a, b, c, d |
e, f, a, b, c, d |
|
e, f, g, h,i |
e, f, g, h, i, d |
e, f, g, h,i, d |
|
e, f, g, h, i, j |
e, f, g, h, i, j |
e, f, g, h, i, j |
| ● | The LDAP Cache feature is applicable only to LDAP-based SIP queries (Control). |
| ● | The maximum LDAP cache size is |
| ● | The device can save up to six LDAP Attributes in the cache per searched LDAP key. |
| ● | The device also saves in the cache queried Attributes that do not have any values in the LDAP server. |
The following procedure describes how to configure the device's LDAP cache globally.
| ● | You can also configure LDAP caching per LDAP Server Group (see Configuring LDAP Server Groups). |
| ● | Before enabling LDAP caching, you must first enable the LDAP service (see Enabling the LDAP Service). |
| ● | To clear the LDAP cache, see Clearing LDAP Cache. |
| ➢ | To enable and configure LDAP cache: |
| 1. | Open the LDAP Settings page (Setup menu > IP Network tab > AAA Servers folder > LDAP Settings). |
| 2. | Select the 'LDAP Cache Service' check box to enable LDAP cache. |

| 3. | Configure the following LDAP caching settings: |
| a. | In the 'LDAP Cache Entry Timeout' field, enter the duration (in minutes) that an entry in the device's LDAP cache is valid. If the timeout expires, the cached entry is used only if there is no connectivity with the LDAP server. |
| b. | In the 'LDAP Cache Entry Removal Timeout' field, enter the duration (in hours) after which the LDAP entry is removed from the device's LDAP cache. |

| 4. | Click Apply, and then restart the device with a burn-to-flash for your settings to take effect. |