REST-Based Management
You can manage the device through the Representational State Transfer (REST) architecture. REST is a Web-based access service, allowing you to access the device's management interface over HTTP/S. Developers can use the device's REST API to integrate the device into their solution and allow administrators to perform management and configuration tasks through automation scripts. The REST API also displays performance monitoring counters.
The REST API relies on a simple pre-defined URL path (<device's OAMP IP address>/api/v1) through which device resources can be accessed. Each resource represents a specific device management element (e.g., file upload), state object (e.g., alarms), or maintenance action (e.g., restart). The REST API uses the standard HTTP/1.1 protocol. Standard HTTP methods (GET, PUT, POST and DELETE) are used to read the resource’s state and to create, update, and delete the resources, respectively. Resource state is described in JSON format and included in the HTTP request or response bodies.
Basic authentication using your login username and password can be used to access the device's REST interface. However, for security, it's recommended to secure REST traffic using HTTPS. For more information, see Configuring Secured (HTTPS) Web and REST Access.
|
➢
|
To access device's REST API interface: |
|
1.
|
Use one of the following methods: |
|
●
|
Third-party REST API client (e.g., Postman):
|
|
i.
|
Configure the top-most endpoint or collection with device's base URL (e.g., https://10.15.7.96/api/v1/). |
|
ii.
|
Configure the required authorization (e.g., basic authentication, bearer token, or mTLS). |
|
i.
|
Start your web browser, and then in the URL field, enter the device's address followed by "/api/v1" (e.g., 10.15.7.96/api/v1); you're prompted to log in with your username and password: |

When using mTLS, you're not prompted for your credentials.
|
a.
|
Enter your credentials, and then click Sign in; the device's REST interface appears, showing the URL paths of the different resource items: |

|
2.
|
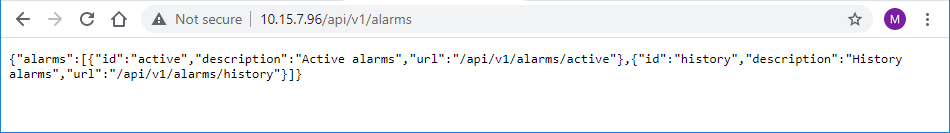
Access the required resource item using the shown URL. For example, to access the device’s alarms resource, append "/alarms" to the URL (i.e. 10.15.7.96/api/v1/alarms). Some items have sub-resources such as the alarms item. When you access the alarms item, the URLs to the active and history alarms resources are shown. |
|
3.
|
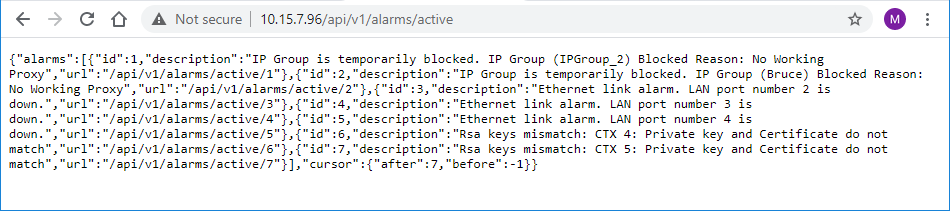
To access a sub-resource (e.g., active alarms) if exists, use the shown URL. For example, to access the active alarms resource, append "/active" to the URL (i.e. 10.15.7.96/api/v1/alarms/active). |
|
●
|
If you know the URL of the resource, instead of accessing each resource menu, you can access it directly using the full URL path (e.g., /api/v1/alarms/active). |



