Configuring Call Setup Rules
The Call Setup Rules table lets you configure up to 64 Call Setup rules. Call Setup rules define various sequences that are run upon the receipt of an incoming call (dialog) at call setup, before the device routes the call to its destination. You can configure Call Setup rules for any call direction - IP-to-IP (SBC), Tel-to-IP, or IP-to-Tel calls. Call Setup rules provide you with full flexibility in implementing simple or complex script-like rules that can be used for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) based routing as well as other advanced routing logic requirements such as manipulation. These Call Setup rules are assigned to routing rules.
Below is a summary of functions for which you can employ Call Setup rules:
|
■
|
LDAP queries: LDAP is used by the device to query Microsoft’s Active Directory (AD) server for specific user details for routing, for example, office extension number, mobile number, private number, OCS (Skype for Business) address, and display name. Call Setup rules provides full flexibility in AD-lookup configuration to suit just about any customer deployment requirement: |
|
●
|
Routing based on query results. |
|
●
|
Queries based on any AD attribute. |
|
●
|
Queries based on any attribute value (alphanumeric), including the use of the asterisk (*) wildcard as well as the source number, destination number, redirect number, and SBC SIP messages. For example, the following Call Setup rule queries the attribute "proxyAddresses" for the record value "WOW:" followed by source number: "proxyAddresses=WOW:12345*" |
|
●
|
Conditional LDAP queries, for example, where the query is based on two attributes (&(telephoneNumber=4064)(company=ABC)). |
|
●
|
Conditions for checking LDAP query results. |
|
●
|
Manipulation of call parameters such as source number, destination number, and redirect number and SBC SIP messages, while using LDAP query results. |
|
■
|
Dial Plan queries: For SBC calls, you can use Call Setup rules to query the Dial Plan table (see Configuring Dial Plans) for a specified key in a specified Dial Plan to obtain the corresponding Dial Plan tag. Call Setup rules can also change (modify) the name of the obtained tag. The device can then route the call using an IP-to-IP Routing rule (in the IP-to-IP Routing table) that has a matching tag (source or destination). You can also associate a Call Setup rule with an IP Group (in the IP Group table). Once the device classifies the incoming call to a source IP Group, it processes the associated Call Setup rule and then uses the resultant tag to locate a matching IP-to-IP Routing rule. You can also use Call Setup rules for complex routing schemes by using multiple Dial Plan tags. This is typically required when the source or destination of the call needs to be categorized with more than one characteristics. For example, tags can be used to categorize calls by department (source user) within a company, where only certain departments are allowed to place international calls.
|
|
■
|
ENUM queries: For SBC calls, you can use Call Setup rules to query an ENUM server and to handle responses from the ENUM server. ENUM translates ordinary telephone numbers (E.164 telephone numbers) into Internet addresses (SIP URIs), using the ENUM's DNS NAPTR records. For example, if the device receives an INVITE message whose destination number is in E.164 format, you can configure a Call Setup rule to query the ENUM server for the corresponding URI address, which is then used in the INVITE's Request-URI. |
|
■
|
HTTP requests (queries): You can use Call Setup rules to query or notify an HTTP/S server, which is configured in the Remote Web Services table (Configuring Remote Web Services). If a response is expected from the server, the query is sent as an HTTP GET or HTTP POST request (configurable). If no response is required from the server (i.e., to notify the server of a specific condition), then an HTTP POST for notifications is sent (configurable). |
|
■
|
Manipulation (similar to the Message Manipulations table) of call parameters (such as source number, destination number, and redirect number) and SBC SIP messages. |
|
■
|
Conditions for routing, for example, if the source number equals a specific value, then use the call routing rule. |
You configure multiple Call Setup rules and group them using a Set ID. This lets you apply multiple Call Setup rules on the same call setup dialog. To use your Call Setup rule(s), you need to assign the Set ID to one of the following, using the 'Call Setup Rules Set ID' field:
|
■
|
(Gateway application) Tel-to-IP routing rules (see Configuring Tel-to-IP Routing Rules)
|
If assigned to an IP Group, the device processes the Call Setup rule for the classified source IP Group immediately before the routing process. If assigned to a routing rule only, the device first locates a matching routing rule for the incoming call, processes the assigned Call Setup Rules Set ID, and then routes the call according to the destination configured for the routing rule. The device uses the routing rule to route the call depending on the result of the Call Setup Rules Set ID:
|
■
|
Rule's condition is met: The device performs the rule's action, and then runs the next rule in the Set ID until the last rule or until a rule whose 'Action Type' parameter is configured to Exit. If this "exit" rule is also configured with a True value for the 'Action Value' parameter, the device uses the current routing rule. If this "exit" rule is configured with a False value for the 'Action Value' parameter, the device moves to the next routing rule. If the 'Action Type' parameter is not configured to Exit and the device has run all the rules in the Set ID, the default of the 'Action Value' parameter of the Set ID is True (i.e., use current routing rule). |
|
■
|
Rule's condition is not met: The device runs the next rule in the Set ID. When the device reaches the end of the Set ID and no "exit" was performed, the Set ID ends with a "true" result. |
You can also configure a Call Setup rule that determines whether the device must discontinue with the Call Setup Rules Set ID and route the call accordingly. This is done using the Exit optional value of the ‘Action Type’ parameter. When used, the ‘Action Value’ parameter can be configured to one of the following:
|
■
|
True: Indicates that if the condition is met, the device routes the call according to the selected routing rule. Note that if the condition is not met, the device also uses the selected routing rule, unless the next Call Setup rule in the Set ID has an Exit option configured to False for an empty condition. |
|
■
|
False: Indicates that if the condition is met, the device attempts to route the call to the next matching routing rule (if configured). If the condition is not met, the device routes the call according to the selected routing rule. |
As the default result of a Call Setup rule is always “true” (True), please adhere to the following guidelines when configuring the ‘Action Type’ field to Exit: If, for example, you want to exit the Call Setup Rule Set ID with "true" when LDAP query result is found and "false" when LDAP query result is not found:
|
■
|
Incorrect: This rule always exits with result as "true": |
'Condition': ldap.found exists
'Action Type': Exit
'Action Value': True
'Condition': ldap.found !exists
'Action Type': Exit
'Action Value': False
'Condition': ldap.found exists
'Action Type': Exit
'Action Value': True
'Condition': <leave empty>
'Action Type': Exit
'Action Value': False
If the source or destination numbers are manipulated by the Call Setup rules, they revert to their original values if the device moves to the next routing rule.
The following procedure describes how to configure Call Setup Rules through the Web interface. You can also configure it through ini file [CallSetupRules] or CLI (configure voip > message call-setup-rules).
|
➢
|
To configure a Call Setup rule: |
|
1.
|
Open the Call Setup Rules table (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > SIP Definitions folder > Call Setup Rules). |
|
2.
|
Click New; the following dialog box appears: |
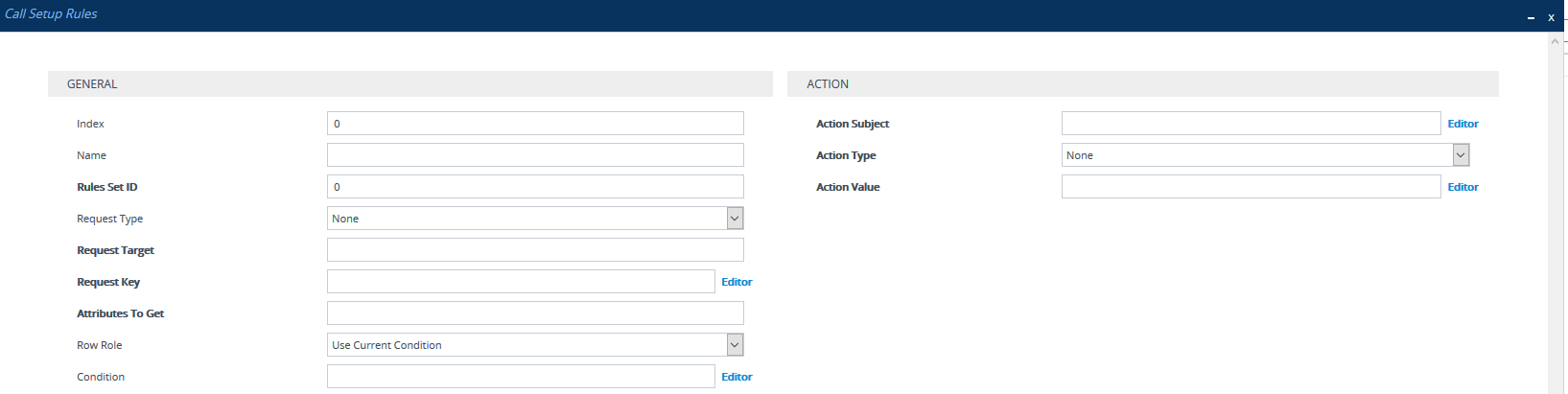
|
3.
|
Configure a Call Setup rule according to the parameters described in the table below. |
|
4.
|
Click Apply, and then save your settings to flash memory. |
Call Setup Rules Parameter Descriptions
|
|
|
| General |
|
|
'Index'
[CallSetupRules_Index]
|
Defines an index number for the new table record.
Note: Each rule must be configured with a unique index.
|
|
'Name'
rules-set-name
[CallSetupRules_RulesSetName]
|
Defines an arbitrary name to easily identify the row.
The valid value is a string of up to 20 characters.
Note: Each row must be configured with a unique name.
|
|
'Rules Set ID'
rules-set-id
[CallSetupRules_RulesSetID]
|
Defines a Set ID for the rule. You can define the same Set ID for multiple rules to create a group of rules. You can configure up to 32 Set IDs, where each Set ID can include up to 10 rules. The Set ID is used to assign the Call Setup rules to a routing rule in the routing table.
The valid value is 0 to 31. The default is 0.
|
|
'Request Type'
request-type
[CallSetupRules_QueryType]
|
Defines the type of query.
|
■
|
[1] LDAP = The Call Setup rule performs an LDAP query with an LDAP server. To specify an LDAP server, use the 'Request Target' parameter (see below). |
|
■
|
[2] Dial Plan = The Call Setup rule performs a query with the Dial Plan. To specify a Dial Plan, use the 'Request Target' parameter (see below). |
|
■
|
[3] ENUM = The Call Setup rule performs a query with an ENUM (E.164 Number to URI Mapping) server for retrieving a SIP URI address for an E.164 telephone number. The ENUM server’s address is the address configured for the 'Primary DNS' (and optionally, 'Secondary DNS') parameters of the IP Interface (in the IP Interfaces table) that is specified in the ‘Request Target’ parameter (see below). For a configuration example, see Call Setup Rule Examples. |
|
■
|
[4] HTTP GET = The Call Setup rule performs an HTTP GET request (query) with an HTTP/S server. To specify an HTTP server, use the 'Request Target' parameter (see below). |
|
■
|
[5] HTTP POST Query = The Call Setup rule sends an HTTP POST request (query) to an HTTP/S server and expects a response from the server. To specify an HTTP server, use the 'Request Target' parameter (see below). |
|
■
|
[6] HTTP POST Notification = The Call Setup rule sends an HTTP POST request to notify an HTTP/S server of a specific condition and does not expect a response from the server. For example, you can configure a rule to notify the server of a 911 emergency call. To specify an HTTP server, use the 'Request Target' parameter (see below). |
|
|
'Request Target'
request-target
[CallSetupRules_QueryTarget]
|
Defines one of the following, depending on the value configured for the 'Request Type' parameter (above).
|
■
|
LDAP: Defines an LDAP server (LDAP Server Group) on which to perform an LDAP query for a defined key. To configure LDAP Server Groups, see Configuring LDAP Server Groups. |
|
■
|
Dial Plan: Defines a Dial Plan (name) in which to search for a defined key. To configure Dial Plans, see Configuring Dial Plans. |
|
■
|
ENUM: Specifies the ENUM server on which to perform the ENUM query. The server is specified by IP Interface name (in the IP Interfaces table). The address of the ENUM server is the address of the 'Primary DNS' (and optionally, 'Secondary DNS') parameters that is configured for the specified IP Interface. If you don’t specify an IP Interface or the specified IP Interface does not exist in the IP Interfaces table, the device uses the OAMP IP Interface. |
|
■
|
HTTP GET, HTTP POST Query, and HTTP POST Notification: Defines the HTTP server to where the device sends the HTTP request. To configure HTTP servers, see Configuring Remote Web Services. |
To configure the key, use the 'Request Key' parameter (see below).
|
|
'Request Key'
request-key
[CallSetupRules_AttributesToQuery]
|
Defines the key to query.
|
■
|
For LDAP, the key string is queried on the LDAP server. |
|
■
|
For Dial Plans, the key string is searched for in the specified Dial Plan. |
|
■
|
For ENUM, the key string is queried on the ENUM server. |
|
■
|
For HTTP GET and HTTP POST queries, the key string is queried on the HTTP server. |
The valid value is a string of up to 100 characters. Combined strings and values can be configured like in the Message Manipulations table, using the '+' operator. Single quotation marks (') can be used for specifying a constant string (e.g., '12345').
You can use the built-in syntax editor to help you configure the field. Click the Editor button located alongside the field to open the Editor, and then simply follow the on-screen instructions.
Examples:
|
■
|
To LDAP query the AD attribute "mobile" that has the value of the destination user part of the incoming call: |
'mobile=' + param.call.dst.user
|
■
|
To LDAP query the AD attribute "telephoneNumber" that has a redirect number: |
'telephoneNumber=' + param.call.redirect + '*'
|
■
|
To query a Dial Plan for the source number: |
param.call.src.user
|
■
|
To query an ENUM server for the URI of the called (destination) number: |
param.call.dst.user
|
■
|
To send an HTTP POST to notify the HTTP server of call connection status: |
'connectionStatus'
Note: The parameter is applicable only if the 'Request Type' parameter is configured to any value other than None.
|
|
'Attributes To Get'
attr-to-get
[CallSetupRules_AttributesToGet]
|
Defines the Attributes of the queried LDAP record that the device must handle (e.g., retrieve value).
The valid value is a string of up to 255 characters. Up to five attributes can be defined, each separated by a comma (e.g., msRTCSIP-PrivateLine,msRTCSIP-Line,mobile).
Note:
|
■
|
The parameter is applicable only if you configure the 'Request Type' parameter to LDAP. |
|
■
|
The device saves the retrieved attributes' values for future use in other rules until the next LDAP query or until the call is connected. Thus, the device does not need to re-query the same attributes. |
|
|
'Row Role'
row-role
[CallSetupRules_RowRole]
|
Determines which condition must be met in order for this rule to be performed.
|
■
|
[0] Use Current Condition = The Condition configured for this rule must be matched in order to perform the configured action (default). |
|
■
|
[1] Use Previous Condition = The Condition configured for the rule located directly above this rule in the Call Setup table must be matched in order to perform the configured action. This option lets you configure multiple actions for the same Condition. |
|
|
'Condition'
condition
[CallSetupRules_Condition]
|
Defines the condition that must exist for the device to perform the action.
The valid value is a string of up to 200 characters (case-insensitive). Regular Expression (regex) can also be used. You can also use the built-in syntax editor to help you configure the field. Click the Editor button located alongside the field to open the Editor, and then simply follow the on-screen instructions.
Examples:
|
✔
|
ldap.attr.mobile exists (if Attribute "mobile" exists in AD) |
|
✔
|
param.call.dst.user == ldap.attr.msRTCSIP-PrivateLine (if called number is the same as the number in the Attribute "msRTCSIP-PrivateLine") |
|
✔
|
ldap.found !exists (if LDAP record not found) |
|
✔
|
ldap.err exists (if LDAP error exists) |
|
✔
|
dialplan.found exists (if Dial Plan exists) |
|
✔
|
dialplan.found !exists (if Dial Plan queried key not found) |
|
✔
|
dialplan.result=='uk' (if corresponding tag of the searched key is "uk") |
|
✔
|
enum.found exists (if ENUM record of E.164 number exists) |
|
●
|
http.response.status == '200' (if the HTTP server responds with a 200 OK) |
|
|
Action
|
|
'Action Subject'
action-subject
[CallSetupRules_ActionSubject]
|
Defines the element (e.g., SIP header, SIP parameter, SIP body, or Dial Plan tag) upon which you want to perform the action if the condition, configured in the 'Condition' parameter (see above) is met.
The valid value is a string of up to 100 characters (case-insensitive). You can use the built-in syntax editor to help you configure the field. Click the Editor button located alongside the field to open the Editor, and then simply follow the on-screen instructions.
Examples:
|
■
|
header.from contains '1234' (SBC application only) |
|
■
|
param.call.dst.user (called number) |
|
■
|
param.call.src.user (calling number) |
|
■
|
param.call.src.name (calling name) |
|
■
|
param.call.redirect (redirect number) |
|
■
|
param.call.src.host (source host) |
|
■
|
param.call.dst.host (destination host) |
|
■
|
dsttags (destination tag) |
|
■
|
header.content-type (for HTTP POST requests) |
|
|
'Action Type'
action-type
[CallSetupRules_ActionType]
|
Defines the type of action to perform.
|
■
|
[-1] None = No action is performed. This option is typically used for HTTP POST requests that are used for notifying the HTTP server (e.g., when the 'Request Type' parameter is configured to HTTP POST Notification). If you configure the parameter to this option and it is the last rule in the table, the device processes the rule and then exits the table. If it is not the last rule, the device processes the rule and then checks the next rule. |
|
■
|
[0] Add = (Default) Adds new message header, parameter or body elements. |
|
■
|
[1] Remove = Removes message header, parameter, or body elements. |
|
■
|
[2] Modify = Sets element to the new value (all element types). |
|
■
|
[3] Add Prefix = Adds value at the beginning of the string (string element only). |
|
■
|
[4] Add Suffix = Adds value at the end of the string (string element only). |
|
■
|
[5] Remove Suffix = Removes value from the end of the string (string element only). |
|
■
|
[6] Remove Prefix = Removes value from the beginning of the string (string element only). |
|
■
|
[20] Run Rules Set = Performs a different Rule Set ID, specified in the 'Action Value' parameter (see below) |
|
■
|
[21] Exit = Stops the Rule Set ID and returns a result ("true" or "false"). |
|
|
'Action Value'
action-value
[CallSetupRules_ActionValue]
|
Defines a value that you want to use in the action.
The valid value is a string of up to 300 characters (case-insensitive). You can use the built-in syntax editor to help you configure the field. Click the Editor button located alongside the field to open the Editor, and then simply follow the on-screen instructions.
Examples:
|
■
|
'+9723976'+ldap.attr.alternateNumber |
|
■
|
application/x-www-form-urlencoded (for HTTP Content-Type header in HTTP requests) |
|
■
|
True (if the 'Action Type' is configured to Exit) |
|
■
|
False (if the 'Action Type' is configured to Exit) |
|
