Configuring Static ARP Table
The Static ARP table lets you configure up to 30 static Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) entries for mapping IP addresses to Media Access Control (MAC) addresses. Instead of dynamically mapping the Layer-3 address to a Layer-2 address, the device uses this table for mapping between these addresses.
| ● | This table is for both IPv4 and IPv6 adresses. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is the IPv6 equivalent of ARP. |
| ● | To view the device's cached and static ARP entries, use the CLI command show network arp. The command's output displays static ARP mappings as "permanent" and dynamic ARP mappings as "reachable". |
The following procedure describes how to configure the ARP table through the Web interface. You can also configure it through ini file [StaticArp] or CLI (configure network > static-arp-table).
| ➢ | To configure static ARP table: |
| 1. | Open the Static ARP table (Setup menu > IP Network tab > Core Entities folder > Static ARP). |
| 2. | Click New; the following dialog box appears: |
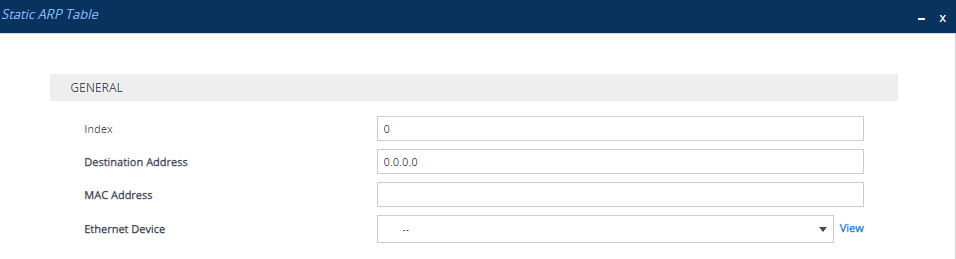
| 3. | Configure a static ARP entry according to the parameters described in the table below. |
| 4. | Click Apply. |
Static ARP Table Parameter Descriptions
|
Parameter |
Description |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
'Index' |
Defines an index number for the table row. Note: Each row must be configured with a unique index. |
||||||
|
'Destination Address' dest-addr [DestAddress] |
Defines the IP address of the destination host or network. By default, no value is defined. Note:
|
||||||
|
'MAC Address' mac-addr [MacAddr] |
Defines the MAC address that is mapped to the IP address specified in the 'Destination Address' parameter. The valid value is in hexadecimal bytes in the format nn:nn:nn:nn:nn:nn (e.g., 00:90:8f:12:13:df). By default, no value is defined. Note: The parameter is mandatory. |
||||||
|
'Ethernet Device' eth-dev [EthDev]
|
Assigns an Ethernet Device from the Ethernet Devices table (see Configuring Underlying Ethernet Devices), which is a VLAN associated with a specific IP interface in the IP Interfaces table. The ARP mapping rule is for packets that the device sends through this Ethernet Device to the specified destination address. |