Configuring SSH Public Key Authentication on Windows
This section describes how to configure SSH public key authentication on Windows, using PuTTY.
The public key cannot be configured with wide characters.
|
➢
|
To configure SSH public key authentication on Windows using PuTTY: |
|
1.
|
Generate private-public keys using PuTTY: |
|
a.
|
Download the PuTTY application (free and open-source terminal emulator). |
|
b.
|
Start the PuTTYgen (PuTTY Key Generator) tool. |
|
c.
|
Under the Parameters group, do the following: |
|
i.
|
Select the RSA or ECDSA option. |
|
ii.
|
In the 'Number of bits in a generated key' field, enter the bit size. |
|
d.
|
Under the Actions group, do the following: |
|
i.
|
Click Generate and then follow the on-screen instructions to generate the public-private key pair. |
|
ii.
|
Click Save private key to save the generated private key to a file (*.ppk) on your PC. |
|
e.
|
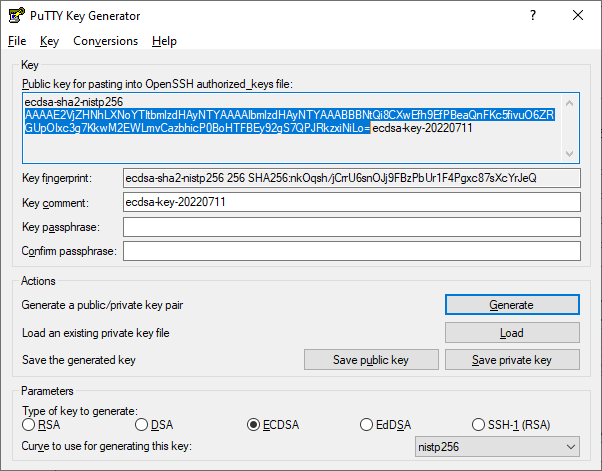
Under the Key group, copy the generated public key string to your clipboard, from after the first space to before the last space, for example: |
|
2.
|
Configure the required user with the generated public key: |
|
b.
|
Select the required user, and then click Edit. |
|
c.
|
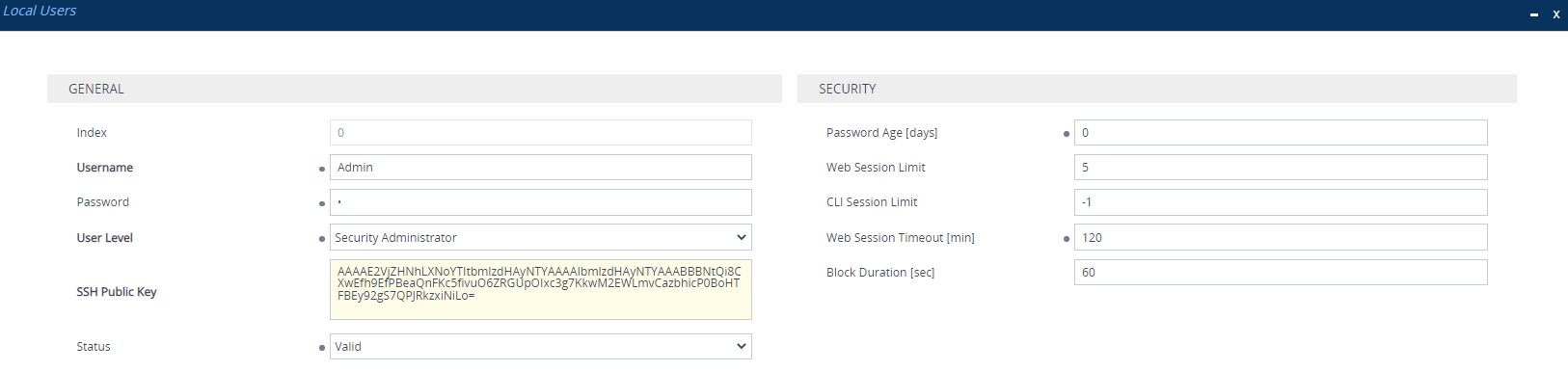
In the 'SSH Public Key' field, paste the public key that you copied previously, as shown in the following example: |
|
d.
|
Click Apply, and then save your settings to flash memory. If you are editing the user that you are currently logged in as, then you are logged out of the Web interface after clicking Apply and need to log in again. |
|
3.
|
Establish an SSH connection with the device: |
|
a.
|
Start the PuTTY application. |
|
b.
|
In the navigation tree, drill down to Connection > SSH > Auth. |
|
c.
|
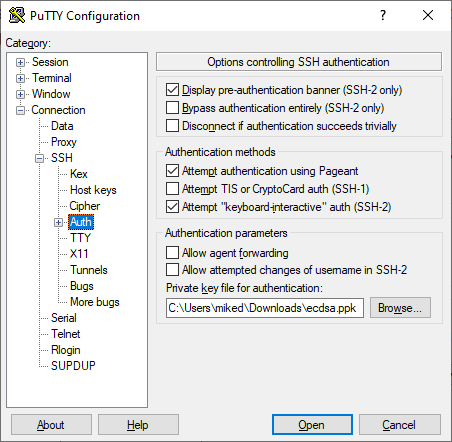
Under the Authentication parameters group, click Browse to select the private key file (*.ppk) that you generated and then saved in Step 1: |
|
d.
|
In the navigation tree, click Session, and then establish an SSH connection with the device. |
When defining the session in PuTTY, make sure that you don't select a saved session that is not associated with the *.ppk key; otherwise, SSH with public key authentication will fail.
|
e.
|
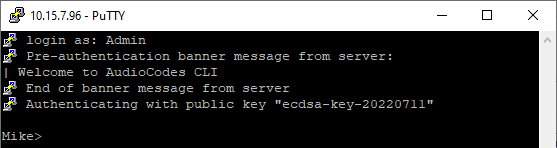
Log in with your username only (e.g., "Admin"); public-private key negotiation occurs for user authentication and if successful, you are logged into the CLI, as shown in the following example: |